|
ISIS Spectrum of
Teide 1
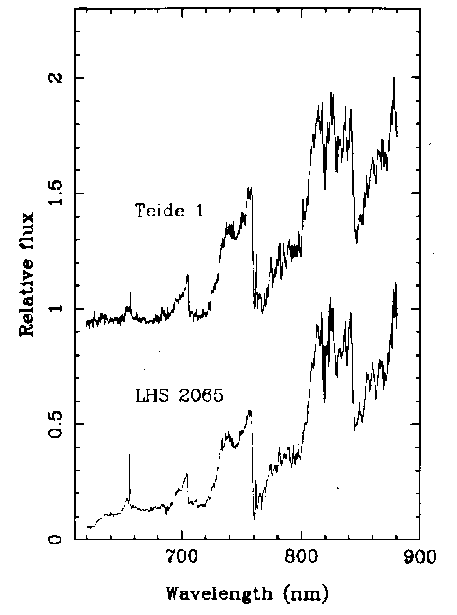
The optical spectrum of Teide 1 (upper trace)
and of the M9 dwarf LHS 2065 (lower trace). The flux scale of both spectra
is normalized to unity at 825 nm. An offset has been added to the spectrum
of Teide 1 for clarity. This spectrum confirmed the discovery of the coldest
quasi-stellar object known in the Universe, the brown dwarf Teide 1. The
spectral lines of neutral potasium between 767-770 nm indicated that it
was an object with high surface gravity, as was expected for a brown dwarf,
and the presence of prominent bands of titanium oxide and, espcially, vanadium
oxide at 750 nm allowed to derive its spectral classification and an estimate
of its effective surface temperature, which turned out to be some 2350
K. [TIFF]
|