| |||
|
| Home > Astronomy > ISIS > Fast Spectroscopy |


|
Fast Spectroscopy1. Preliminaries
Two E2V electron multiplying ‘Low-Light-Level’ L3CCDs (i.e. the QUCAMS) are available for use on the red and blue arms of ISIS to do fast of faint-object spectroscopy. Both detectors are identical with 1k×1k, 13 microns/pixel, full frame transfer device, and can be used in two multiplying modes: slow or fast. In the fast mode the read-out-noise is nearly zero. Exposure times shorter than 1s are possible with almost no dead times (20 miliseconds per full transfer) as the system continuously expose while reading the previous image. The technical characteristics of QUCAM2 and QUCAM3 are summarized here (note that both detectors are nearly identical). The detectors have very good cosmetic characteristics, and excellent quantum efficiency. 2. The L3CCD
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ISIS wavelength coverage and resolutions with
QUCAM2/3 in the blue arm
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grating
|
Blaze
|
Dispersion (Å/mm)
|
Dispersion (Å/pix)
|
Total Spectral range (Å)
|
Unvignetted range (1024 pixels)
|
Slit-width for 54 mu at detector (in arcsecs)
|
Slit-width for 27 mu at detector (in arcsecs)
|
|
R158B
|
3600
|
120
|
1.56
|
1597
|
1597
|
0.8
|
0.4
|
|
R300B
|
4000
|
64
|
0.83
|
850
|
850
|
0.8
|
0.4
|
|
R600B
|
3900
|
33
|
0.43
|
440
|
440
|
0.9
|
0.45
|
|
R1200B
|
4000
|
17
|
0.22
|
225
|
225
|
1.1
|
0.55
|
|
H2400B
|
Holo
|
8
|
0.11
|
113 |
113
|
1.2
|
0.6
|
|
ISIS wavelength coverage and resolutions with
QUCAM2/3 in the red arm
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grating
|
Blaze
|
Dispersion (Å/mm)
|
Dispersion (Å/pix)
|
Total Spectral range (Å)
|
Unvignetted range (1024pixels)
|
Slit-width for 54 mu at detector (in arcsecs)
|
Slit-width for 27 mu at detector (in arcsecs)
|
|
R158R
|
6500
|
121
|
1.57
|
1608
|
1608
|
0.84
|
0.42
|
|
R316R
|
6500
|
62
|
0.81
|
829
|
829
|
0.88
|
0.44
|
|
R600R
|
7000
|
33
|
0.42
|
430
|
430
|
0.97
|
0.48
|
|
R1200R
|
7200
|
17
|
0.26
|
266
|
266
|
1.24
|
0.62
|
Observing with the QUCAMs on ISIS is very similar to normal CCDs (see ISIS Cookbook). But some differences related only to the CCD operation are discussed below.
4.1 Settings.
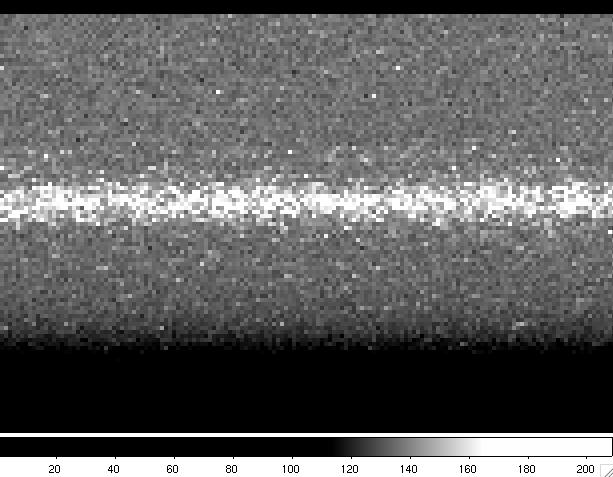
The spectral direction used with the QUCAMs is the x-axis. Windowing in the y-axis make read-out faster. To have enough sky at both sizes of a point-like source we used a window of 100 pixel width in y-axis and covering the whole range of the x-axis. In our tests we used
SYS> window 1 qucam2 "[1:1072,540:639] "
Windowing also in the x-axis permits shorter exposure times but the spectral range of the spectrum will be also shorter.
4.2 Taking spectra of the target.
All UltraDAS commands can be used as with the other CCD. But to continuously expose while reading the previous image the command to be used is rsrun.
rsrun performs a sequence of exposures for rapid spectroscopy on the camera, reads them out and saves the data in a FITS file containing the exposures in a sequence of FITS extensions. The file is passed to the archiving and logging facilities.
A title may be given for the observation: the title appears as the datum of the OBJECT keyword in the FITS headers and as the target name in the observing log. If no title is given, the system attempts to read the target name from the Telescope Control System (TCS): this makes the value for the OBJECT keyword the same as that for the CAT-NAME keyword. If the TCS does not respond, then the title defaults to "(object not named)".
rsrun [<camera>|<instrument>] <number-of-exposures> <exposure-time> ["<title>"]
multrsrun [<camera>|<instrument>] <n-obs> <number-of-exposures> <exposure-time>
where number-of-exposures is the required number of exposures in the sequence, exp-time is in seconds and n-obs is the number of cycles in a multrsrun. The title-string must be enclosed in double quotes.
Example:
rsrun red 127 1 "rapid spectroscopy run"
performs a series of 127 one second integrations.>
Note that the mechanical shutter is always open, thus if you use exp-time=0 the real exp. time depends on the time needed to make the full frame transfer (0.229s using a [1:1072,540:639] window)
A problem detected using rsrun is that the exposure-time of the individual images is not perfectly constant (see Fig. 3). As the camera is used with UltraDAS and this is not a real-time system, the full-frame transfer time depends on the other tasks the computer is running during the read-out process. This has to be taken into account when combining images to attain the final needed exposure time.
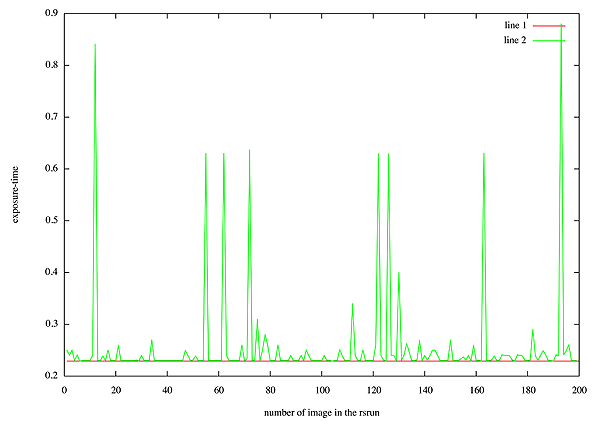
Fig. 3: Exposure time of the 200 individual images obtained using the rsrun command and 0 exposure-time. The plotted exposure time is measured as the difference between the utstart of two sucesive images. The red line corresponds to 0.229s, the minimum exposure time measured. Notice that the exposure time is not constant.
4.3 Bias, flats, arcs.
Arcs and bias can be obtained in the usual way. Flat fields have to be obtained at low-signal levels (less than 10000 ADUs), so to attaing good S/N several flat fields are needed.
| Top | Back |
|