
deviceControl Record Reference Manual

This document describes the deviceControl record created by the Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics.

This document describes the deviceControl record created by the Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics team for integrated control of direct current (DC) and Stepper Motor positioned devices.
This document defines the interface to the deviceControl record only. For a list of EPICS records created by and for the GEMINI project see the Gemini Record Reference Manual [3]. For a complete list of the standard EPICS records, and a description of the field summary tables, refer to the EPICS Input Output Controller Record Reference Manual [1].

This section will provide an overview of the record functions, then a field summary for the record. The next section is a configuration section on how to configure this record, followed by a section detailing the operation of the record. Finally there is a section on details for the support modules that make up this record.
This record has been designed to provide a higher level of moving device control than the standard Motor or Steppermotor records. As well as controlling device position it also incorporates the functionality of the Gemini CAD and CAR records [3] to allow checking of input arguments before they are applied and monitoring the motion command status.
The deviceControl record communicates directly with the selected motor drive interface electronics via integrated device support. Current device support is limited to Oregon Micro Systems OMS 8 and OMS 44 VME boards.
General features of the deviceControl record include:
New motion parameters (position, velocity etc.) are loaded into the record and the appropriate operating mode selected. The GO directive is then issued to begin the following motion sequence:
Any errors detected in the above will generate a diagnostic message explaining what happened as well as causing the motion to abort.
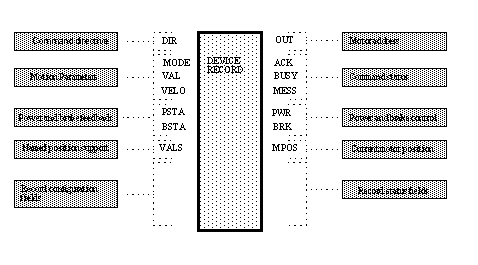
See Device Control Record - Primary operating fields shows the primary deviceControl record fields which are available from a configuration tool (e.g. CAPFAST).
|
Figure 2 shows the permitted state transitions for the deviceControl record. This provides a general synopsis of the standard operational control flow.
See Field Summary is a summary of fields for a record instance. All of these fields, plus additional standard fields (see See Additional Standard Record Fields) defines the record structure that is accessed via the module code. Column 3 (DCT) indicates if the field will appear in a configuration tool, column 5 (Access) indicates if the field can be read, column 6 (Modify) indicates if a field can be written to, column 7 (Rec Proc Monitor) indicates if the field can raise a monitor, and column 8 (PP) indicates that changes to the field causes the record to be processed if set to Yes.
The field, brief description and type for the fields are listed in See Field Descriptions. Some more detailed field descriptions can be found in See Configuration See Configuration.

This record does not require any record or device support code changes to make it function. It currently will work with both the OMS8 and OMS44 board. PLEASE NOTE: that this record works similar to the EPICS motor record and assumes control of the boards attached to it. As a result, this record and the motor record will not be able to run on the same IOC. See Configuration Field Descriptions gives a list of all configurable record fields. These fields can be accessed via the CAPFAST symbol. See Status Field Descriptions contains a list of status record fields and a detailed list of the results they represent.
|
Set the acceleration/deceleration rate for all motions in Engineering Units/Sec2. Motor velocity is ramped linearly from VBAS to VELO Engineering Units/sec at the beginning of a motion and from VELO to VBAS at the end of a motion. If the distance to be moved is less than that covered by the two ramps, the ramps are automatically adjusted by the motor driver hardware. |
||
|
Set the brake control timeout. If this value is non-zero the record will execute the brake control sequence(). A BTMO value of zero causes the record to proceed directly from the powering-up to starting state. |
||
|
Name of device support to use. Default and only valid value is: |
||
|
Set the encoder deadband. If encoder feedback is enabled (see UEIP), all encoder value changes less than +/- EDBD around the value at the end of the last motion will be ignored by the record. Once this threshold has been crossed all encoder changes will be recognized by the read. |
||
|
Set the string to be displayed by a dm engineering screen units request. |
||
|
Set the encoder resolution. The value should be the number of encoder counts per engineering units. i.e., if the device moves 2mm for every shaft rotation and there are 2.00 encoder counts per revolution the ERES field should be set to 2000/2 or 1,000 for engineering units of millimeters. (not yet implemented) |
||
|
Set the indexing algorithm. When executing a mode of INDEX, the algorithm used will depend on the value of the IALG field as follows: 0 = Index is none (this acts like a move and works well during debugging. It will move to the VAL field value ) 1 = Index to Lower home switch or in reverse. 2 = Index to Upper home switch or forward. 3 = Index to center. This will move forward until it hits a lower limit switch and then move up till it hits a home switch. 4 = Index to lower limit switch. 5 = Index to upper limit switch. See the INDEX section for details of these indexing algorithms. |
||
|
Set the motion deadband. Motion requests to positions +/- the MDBD value of the current position will be acknowledged as completed but no actual device motion will take place and the position feedback fields will continue to show the current position. |
||
|
Set the motor resolution. The value is given as the number of motor steps per engineering units. i.e. if the device moves 2mm for every rotation of the shaft and there are 200 steps/revoluation then the MRES field should be set to 200 steps/2mm or 100 for engineering units of mm. |
||
|
Select the motor to be controlled. This is a VMEIO link with the following format "#Cx Sy" where x is the OMS interface card number (0-7) and y is the channel on the card that the motor is connected to. |
||
|
Set the maximum position for the device in engineering units. Motion request to positions (VAL) greater than this value will be rejected. |
||
|
Set the minimum position for the device in engineering units. Motion request to positions (VAL) less than this value will be rejected. |
||
|
Set the power control timeout. If the value is non-zero the record will enable the power control sequence (See Power Control). A PTMO value of zero causes the record to stop the power control sequence. |
||
|
This turns the power on and off. A PWR value of zero causes the record to proceed directly from the powering-up to unlocking state. |
||
|
Set the source directory for the translation file. If this field is left blank then no named positions translation is performed. |
||
|
Set the name of the translation file. If the field is left blank then no named position translation is performed. The format of the file is: # Lines beginning with a "#" sign is a comment # Named Position target(VAL) OR index type You can either give a named position a target - which will cause the mode to be "MOVE", and set the VAL to the target, or you can make the named position mean a mode of "INDEX" where the index algorithm is specified in the last column. |
||
|
Only uses this if PTMO is set. A nonzero value will enable the control of motor power via the motor drive electronics auxiliary power bit. |
||
|
Set the brake feedback checking mode. If this field is non-zero then the brake status bit (BSTA) will be checked whenver the external brake state is changed (see BTMO) to confirm that the action has taken place. Failure of the status bit to reflect the desired state will cause the motion to be aborted. |
||
|
Set the encoder feedback mode. A non-zero value will cause the encoder value to be read (if the interface hardware supports encoders for this motor) and used for stall and motor-creep detection. |
||
|
Set the power feedback checking state. If the field is non-zero then the power status bit (PSTA) will be checked whenever the power status is changed (see PTMO) to confirm that the action has taken place. Failure of power during motion or failure of the status bit to reflect the desired power state will cause the motion to be aborted. |
||
|
Set the base velocity in engineering units/second.. This is the minimum velocity that the device will move at. Acceleration/deceleration profile will start/end at this velocity. Target velocities less than this value will actually be performed at the VBAS velocity. |
||
|
Set the target velocity. All device motions will be performed at this velocity, specified in Engineering Units per second. |
||
|
Set the maximum velocity. Any motion requests with the VELO field set greater than this value will be rejected. |
||
|
Set the minimum velocity. Any motion requests with the VELO field set less than this value will be rejected. |

deviceControl record operation is controlled by the DIR, MODE and Primary motion control fields (VAL, VALS, MODE and VELO). In normal operation, motion parameters are written to the appropriate control fields and the GO directive is issued to begin execution of the command. If a motion sequence involving more than one device is being prepared it will be possible to check the validity of the control information via the CHECK directive for all devices prior to starting the motions.
Commands to re-position a device are sent via the DIR field. While a command is being processed the BUSY field is set to BUSY. When a command has completed the BUSY field is set either to IDLE (if all went well) or ERR (if something went wrong). In some cases, a command in progress can be updated with new information as described below. A directive that requires no asynchronous processing (such as a STOP when the device is already idle) will be acknowledged by setting the BUSY field to BUSY for a short period of time then returning it to IDLE.
This directive terminates a command in progress. Any moving devices will be stopped in a controlled manner prior to setting the record to IDLE. The STOP directive will simply be acknowledged if the record is idle.
This directive validates all of the input fields prior to starting or updating a command. The ACK field is set to zero if all arguments are within limits and it is safe to start or update a command. If the command is rejected (ACK set to nonzero) a diagnostic message appears in the MESS field to explain why. The CHECK directive does not affect the state of the record BUSY field.
This directive either starts a new command action or updates the control parameters for a command in progress. All input fields are validated prior to executing the command (see CHECK). If it is safe to proceed the record is set to BUSY and the control information is processed according to the current state of the record. The record will remain BUSY until either the command has completed or an error is encountered.
When a device motion command has been received the operating mode field is consulted to determine how to process the command.
Possible MODE field values are:
Initialize the device. The initialization process consists of:
The INIT command will be rejected if the device is in motion.
This is the normal operating mode for the record. It calls for the device to be powered up and unlocked, moved to a new target and shut down again ready for the next motion command. If the given target position is within the motion deadband of the current motor position the command will simply be acknowledged without moving the motor. New motion parameters (such as velocity and target updates) can be issued while the device is still in motion and they will be acted upon immediately if the GO directive is re-issued.
In TRACK mode the device is powered up and unlocked (if not already active) however the device will be left unlocked and powered on after the motion is completed. This mode is useful when the device must follow a series of target positions with the minimum delay. New motion parameters (such as velocity and target updates) can be issued while the device is still in motion and they will be acted upon immediately.
In INDEX mode the target position is ignored and the device is sent to find its home or reference point. How this is accomplished depends on the current setting of the Index Algorithm (IALG) field as follows:
If the homing sequence was successful, the Home Position Valid (HPVL) field will be set to non-zero to indicate that the reference point is valid.
The deviceControl record supports the concept of named positions. This is a useful feature for fixed position devices (such as filter wheels or in/out devices) where the target position can be given in terms of the fixed position name rather than the actual position in engineering units.
Named position support is implemented via the VALS field. An ascii string written to this field will trigger a search of the associated lookup table. If a named position corresponding to the string is found in the table the associated target position in engineering units is written into the VAL field and will be acted upon when the GO command is issued. If the string can not be translated the command will be rejected when the GO command is issued.
This feature allows the device to be positioned to its valid positions only and relieves the controlling process from having to know how these positions are implemented.
The lookup table is contained in an ASCII file (see the TDIR and TFIL field descriptions). This file is loaded into an internal lookup table whenever the record is initialized. The file can be changed and re-loaded at any time via the INIT command.
Integral to the deviceControl record is the optional control of motor power and locking mechanisms. When a motion command is received the power control sequence is executed followed by the brake control sequence prior to starting the motion. In TRACK mode the power is left on and brake off following a move. In all other modes the brake control sequence is executed followed by the power control sequence when the move is completed. Disabling one or both features will simply skip that part of the sequence with no other effect on record operation.
Power to the motor can be controlled in one of two ways: internal (using device support) and external (using other EPICS records). If external power feedback is available it can be checked to insure that the power has responded before moving on to the brake control phase. The general sequence is as follows:
External locking devices are controlled via external EPICS records triggered by the BRKL field. If locking device feedback is available it can be checked to insure that the device has responded before actually starting the motion. The general sequence is as follows:
All definitions for encoded fields are device support independent. Currently these are given, along with appropriate mnemonics, in the module header file recDeviceControl.h.

The following section will define the support routines for both the record and device support modules.
The record support routine, as defined by deviceControlRSET, is the same for every record of this type. The associated functions are:
This routine is called twice at iocInit. On the first call it returns immediately. On the second call, it does the following:
This routine implements the following algorithm:
Returns the engineering units string for display purposes.It returns the value in the EGU field.
Status buttons (FLT) are treated like callbacks and so set the internal callback processing flag to prevent processing of other external fields.
The graphic display range limits are set to the values of the PHLM/PLLM fields for the VAL and MPOS fields.
The deviceControl record has been written to be as device-independent as possible. It requests only basic motion functions from the drive support code.
The device support routine, as defined by deviceControlDSET, is the same for every record of this type. The associated functions are
This function is called twice during initialization of the IOC. On the first pass (before records are initialized) the scan task is started and the linked list of subscribing records is initialized. The second pass (after records are initialized) is ignored.
This function is called once for each deviceControl in the system. It creates and initializes a private motion control structure for the record's device support and adds it to the list of control structures to be scanned by the scan task. The control structure is saved in the calling record's device private structure to allow scan task callbacks to re-process the record.
This function transfers the motion control variables from the communications structure to the private control structure and writes them to the hardware as appropriate.
This function starts, stops or aborts device motion as directed by the mode word supplied. How this is done is entirely up to the device support.
This function enables or disables the motor power according to the power word supplied using the motor control electronics. How this is done is entirely up to the device support.
All command and status information is passed via the record's device private structure. This communications structure is defined in the header file recDeviceControl.h as follows:
SEM_ID mutexSem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
void pPrivate; /* device support private structure pointer */
long callback; /* (status) set to TRUE for callback processing */
long timeout; /* (status) set to TRUE for delay callback */
long target; /* (command) desired target position (steps) */
long velocity; /* (command) desired motion velocity (steps/sec) */
long acceleration; /* (command) desired acceleration time (steps/sec2)*/
long index; /* (command) index algorithm */
long position; /* (status) current device position (steps) */
long encoder; /* (status) current encoder value (encoder units) */
long moving; /* (status) current motion state */
long limit; /* (status) current limit switch state */
long status; /* (status) current device support status */
long simulation; /* (command) desired simulation mode */