 . The components are as follows:
. The components are as follows:



TAURUS-2 is the second generation instrument inspired by the success of the original TAURUS-1 wide-field imaging Fabry-Perot interferometer. The instrument was re-designed as a common-user facility and built under contract for both the WHT and the AAT by the Kapteyn Sterrenwacht, Roden.
A major design goal of TAURUS-2 was that, unlike TAURUS-1, it should be a straightforward and flexible instrument to use. In order that the instrument can be reconfigured easily, it is possible to change remotely between a wide range of filters, etalons and apertures.
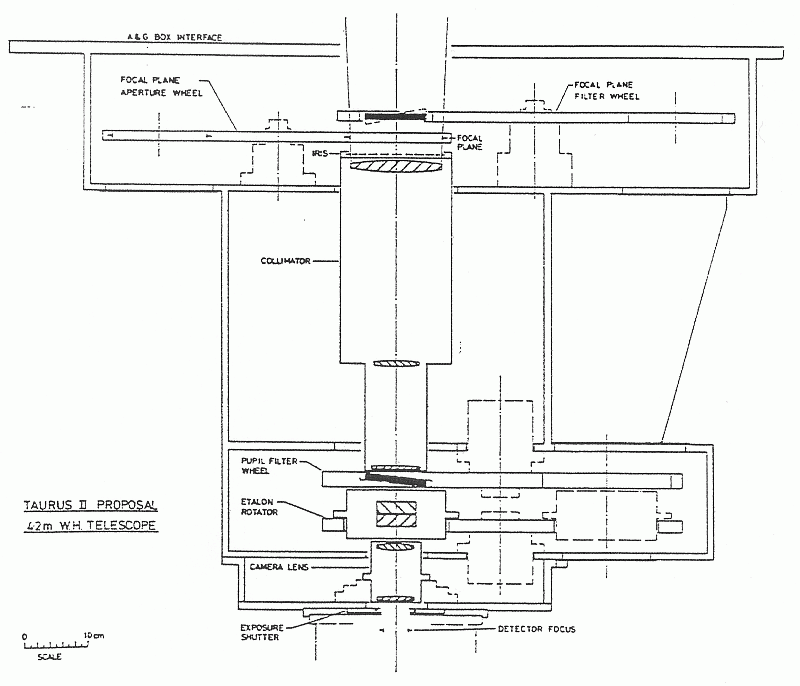
The major optical components of TAURUS-2 are shown schematically in
Figure  . The components are as follows:
. The components are as follows:
[ TIFF ]
Figure: TAURUS-2
 . The filters
can be tilted remotely by up to 10 in order to shift the
central wavelength to the blue (see 5.10.5).
. The filters
can be tilted remotely by up to 10 in order to shift the
central wavelength to the blue (see 5.10.5).
 lists the aperture masks currently
available.
lists the aperture masks currently
available.
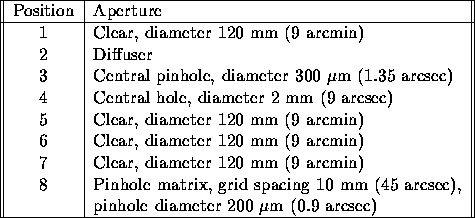
Table: TAURUS-2 aperture masks
 .
.
 /2 (one order) step
input is about 300
microseconds. Typical performance of the system is such that a
'mechanical' finesse
N > 50 can be maintained almost indefinitely. The Fabry-Perot etalons
available are listed in Table
/2 (one order) step
input is about 300
microseconds. Typical performance of the system is such that a
'mechanical' finesse
N > 50 can be maintained almost indefinitely. The Fabry-Perot etalons
available are listed in Table  . Note that the set of etalons
previously advertised as being available for observations with
TAURUS-1 cannot be used in TAURUS-2.
. Note that the set of etalons
previously advertised as being available for observations with
TAURUS-1 cannot be used in TAURUS-2.
TAURUS--2 can be used with either the CCD-IPCS photon counting detector or a CCD. The question of which detector should be used for a given programme is discussed below.