Zenith distance < 70
- 6 h < hour angle < + 6 h (above pole)
Declination > -30 09 30
30
Operation below the pole is possible, but only gains a small extra area of sky; consider it in exceptional circumstances.
Note that the lower windshield causes vignetting for zenith distances > 57 and is raised for such observations.
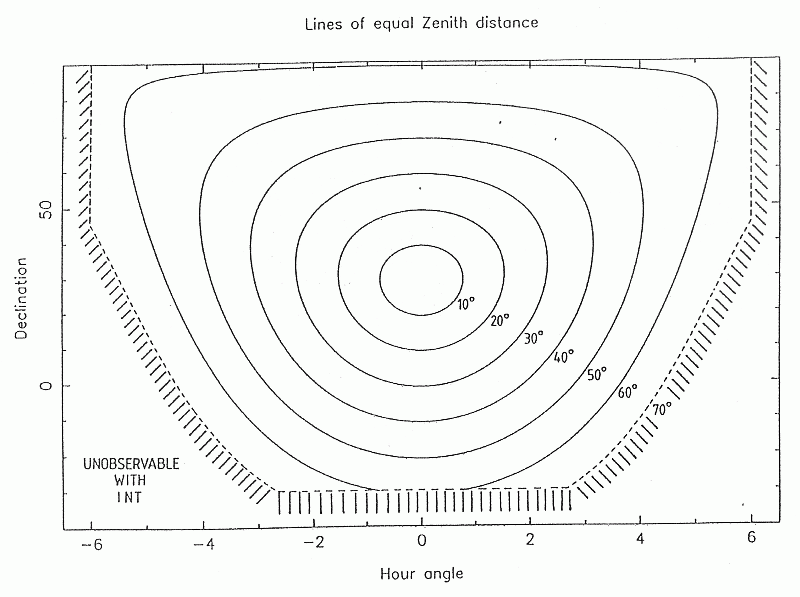
Figure  shows the area of the sky normally accessible to the INT.
shows the area of the sky normally accessible to the INT.
[ TIFF ]
Figure: The
area of sky accessible to the INT. Lines of equal
zenith distance are drawn on a plot of declination against hour angle.
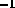 and 1.3 s
and 1.3 s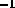 respectively.
respectively.
Pointing accuracy: rms residual of a global fit = 5 arcsec
Tracking accuracy:
(unguided) < 1 arcsec in 3 minutes; < 2 arcsec in 10 minutes
(guided) < 0.3 arcsec
Offsetting accuracy: Less than 1 arcsecond using the AUTOFFSET command.