

Next: Performance.
Up: Low Dispersion Survey
Previous: Overview
Fig.  shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table
shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table  summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.
summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.
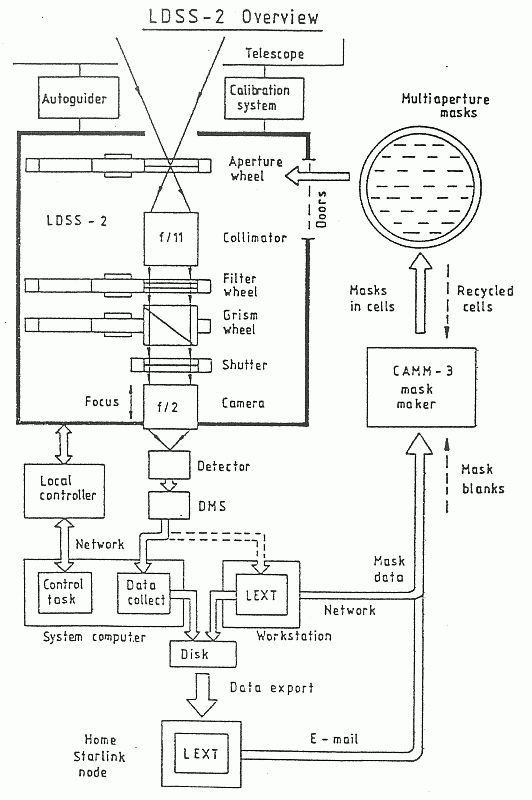
[ TIFF ]
Figure: Schematic of LDSS-2
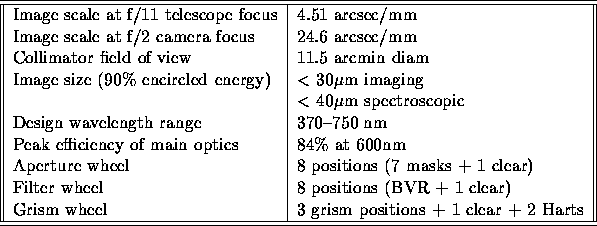
Table: Summary of LDSS-2
The principle components are:
- Aperture Wheel.
The telescope is focussed onto a multiaperture mask so that light
passes through the apertures cut in the mask and enters the
collimator.
The masks are held in an 8-position wheel, allowing simple and quick
changes between different masks.
The multiaperture masks consist of a number of holes and slits
(typically 330
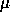 m wide = 1.5 arcsec) cut in a brass disk.
The masks can be made at the telescope close to the time of
observation, using a specialized manufacturing facility which provides
masks of very high quality.
m wide = 1.5 arcsec) cut in a brass disk.
The masks can be made at the telescope close to the time of
observation, using a specialized manufacturing facility which provides
masks of very high quality.
- Collimator. The collimator converts the input f/11 beam
into parallel light, before passing it through a filter and grism.
The field of view has a diameter of 11.5 arcmin.
- Grism Wheel. Four grisms are provided of which 3 can be
mounted in the grism wheel at any one time.
These cover a range of spectral resolution 200 < R < 1000, where
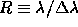 (see table
(see table  ).
).
- Filter Wheel. Up to 7 filters can be mounted in the filter
wheel.
Three broad-band filters (the BVR Harris set as used by NOAO) are
provided together with 3 other filters designed for use in
spectroscopic mode to suppress unwanted orders.
- Camera. The light is then focussed by the camera onto an
external detector with a final focal ratio of f/2, giving an image
scale of 24.6 arcsec/mm over a field of view with 11.5 arcmin diam.
By using clear positions in the aperture and grism wheels, LDSS-2 can
be used to give direct images in the chosen filter passband.
The image size for 90% encircled energy is < 30
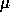 m in
direct imaging mode, and
m in
direct imaging mode, and  m in spectroscopic mode.
m in spectroscopic mode.
- Detector. LDSS-2 is normally used with the Tektronix
1024 CCD. In direct imaging mode this covers a 10.1 arcmin square field
with an image scale of 0.59 arcsec/pixel.
- Software. An integral part of LDSS-2 is the LEXT software
package which allows the observer to design the aperture masks,
acquire the target fields and reduce the data.
LEXT is a Starlink-compatible program which runs on a workstation at
the telescope but can also be used at Starlink nodes.



Next: Performance.
Up: Low Dispersion Survey
Previous: Overview
Tue Aug 15 16:42:46 BST 1995
 shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table
shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table  summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.
summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.



 shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table
shows a schematic diagram of LDSS-2 and
Table  summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.
summarizes the main properties of the
instrument.

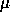 m wide = 1.5 arcsec) cut in a brass disk.
The masks can be made at the telescope close to the time of
observation, using a specialized manufacturing facility which provides
masks of very high quality.
m wide = 1.5 arcsec) cut in a brass disk.
The masks can be made at the telescope close to the time of
observation, using a specialized manufacturing facility which provides
masks of very high quality.
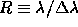 (see table
(see table  ).
).
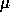 m in
direct imaging mode, and
m in
direct imaging mode, and 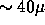 m in spectroscopic mode.
m in spectroscopic mode.