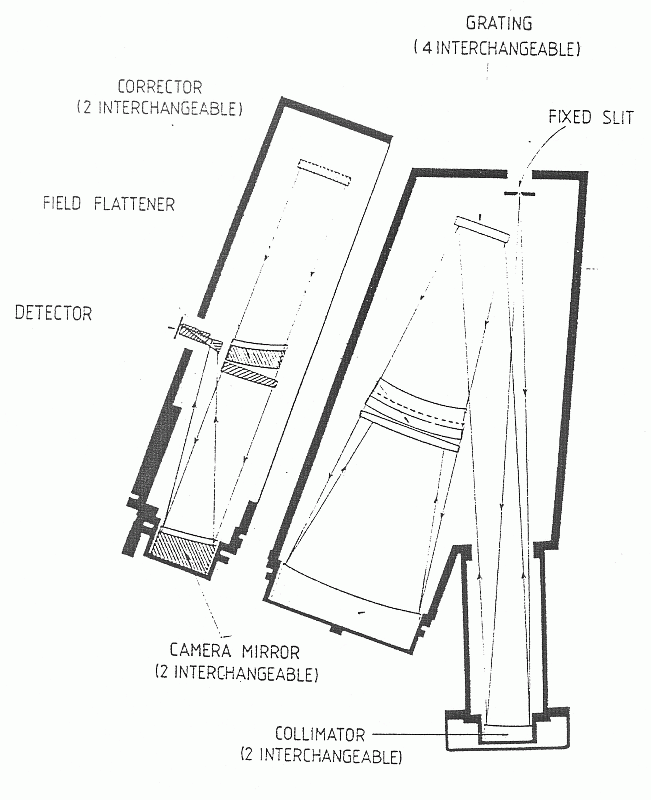
 shows schematically the main optical components of the spectrograph. These
are:
shows schematically the main optical components of the spectrograph. These
are:



In the following description the telescope is assumed to be parked pointing to
the zenith, with the spectrograph mounted. Figure  shows schematically the main optical components of the spectrograph. These
are:
shows schematically the main optical components of the spectrograph. These
are:
The following Schott glass colour filters are available: BG28, BG38, UG1, GG385, GG395, GG495, RG630, RG695, RG830. Filters are 25 mm in diameter and 2.5 mm thick.
Two ND filters, 25 mm in diameter and 2 mm thick, are available: ND=1.42, 3.0.
The slit assembly is interchangeable so as to allow the
use of a number of slits of fixed width. Two slits are available, of
widths 73 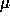 m and 110
m and 110 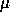 m (1.0 and 1.5 arcsec respectively).
For a typical
slit-to-detector reduction factor of about 4.1 (weakly dependent on
the angle of incidence on the grating) these slit
widths project to approximately 18
m (1.0 and 1.5 arcsec respectively).
For a typical
slit-to-detector reduction factor of about 4.1 (weakly dependent on
the angle of incidence on the grating) these slit
widths project to approximately 18 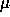 m and 27
m and 27 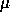 m at the detector.
Access to
the slit assembly and optical components is by removing the
side-panel. The slit position angle can only be set manually by
rotating the instrument turntable with the telescope at zenith park.
m at the detector.
Access to
the slit assembly and optical components is by removing the
side-panel. The slit position angle can only be set manually by
rotating the instrument turntable with the telescope at zenith park.
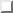 below. Gratings are 57 mm
below. Gratings are 57 mm 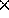 57 mm
57 mm 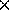 10 mm in size.
The gratings are mounted with three M3 bolts onto a turntable, and a
tangent screw on each grating assembly ensures precise location of
the grating relative to the turntable. Grating angle is selected
by manual rotation of the turntable using a calibrated knob and a
scale with vernier. The ``Richardson-Brealey Spectrograph Manual''
(La Palma User Manula XI)
gives details of the dependence of central wavelength, dispersion and
slit-to-detector reduction factor on grating angle (Note - the new
tables should be used as given in the supplement).
10 mm in size.
The gratings are mounted with three M3 bolts onto a turntable, and a
tangent screw on each grating assembly ensures precise location of
the grating relative to the turntable. Grating angle is selected
by manual rotation of the turntable using a calibrated knob and a
scale with vernier. The ``Richardson-Brealey Spectrograph Manual''
(La Palma User Manula XI)
gives details of the dependence of central wavelength, dispersion and
slit-to-detector reduction factor on grating angle (Note - the new
tables should be used as given in the supplement).

Table: Characteristics of gratings for the Richardson Brealey Spectrograph
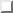 ). The focal length is 208 mm.
Like the collimator, the camera mirror and two correcting elements
are interchangeable and two sets are available with coatings
which maximise efficiency in the blue and red spectral regions
respectively. The red set of optics makes better use of the red sensitivity
of the CCD and can be used to the blue cut-off with some loss of
efficiency. Focussing of the spectrograph is achieved by movement
of the camera mirror, controlled by a micrometer screw on the camera
mirror assembly. A Hartmann mask, located on the slide in front of
the collimator, allows the best focal position to be set with
an accuracy of
). The focal length is 208 mm.
Like the collimator, the camera mirror and two correcting elements
are interchangeable and two sets are available with coatings
which maximise efficiency in the blue and red spectral regions
respectively. The red set of optics makes better use of the red sensitivity
of the CCD and can be used to the blue cut-off with some loss of
efficiency. Focussing of the spectrograph is achieved by movement
of the camera mirror, controlled by a micrometer screw on the camera
mirror assembly. A Hartmann mask, located on the slide in front of
the collimator, allows the best focal position to be set with
an accuracy of 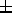 50
50 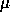 m.
m.
[ TIFF ]
Figure: The JKT Richardson-Brealey Spectrograph