

Next: Performance
Up: Faint Object Spectrograph
Previous: FOS-1
The design of the original FOS was adapted to the WHT by Sue Worswick.
The main components are as follows:
- Slit unit and dekker slide.
- FOS-2 uses the same slit unit and
dekker slide as ISIS (see Section
 ).
).
- The grism
- has a 150 lines/mm plane transmission grating on the
front surface. A ray from the slit centre to the centre of the
grating surface makes an angle of 6.892 degrees with the normal
to the surface and with the normal to the grating rulings. The
central ray at a wavelength of 8000Å is diffracted normal to the
grating. The grism as a whole is a cemented assembly of the
transmission grating, cross dispersing prisms of Schott SK5 and
LF5 glass, and an aspheric corrector plate of Schott K10 glass.
- The camera mirror
- is coated with an extended blue response silver
coating and is expected to keep its high reflectivity, as the
system is not let up to atmospheric pressure, except for
maintenance.
- Camera.
- This has a focal ratio of f/1.4 giving a slit to
detector reduction factor of 7.8. The dispersion at the detector
is 400 Å mm
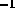 in first order and 200 Å mm
in first order and 200 Å mm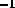 in second order.
The camera consists of an aspheric corrector plate cemented
to the underside of the grism/prism assembly and the silver-coated
spherical mirror. A field flattening lens produces a flat focal
plane at which the detector surface is located. The detector
package is small enough to fit within the shadow of the
telescope's secondary mirror to minimize obscuration losses.
The optical system has a resolution of 33
in second order.
The camera consists of an aspheric corrector plate cemented
to the underside of the grism/prism assembly and the silver-coated
spherical mirror. A field flattening lens produces a flat focal
plane at which the detector surface is located. The detector
package is small enough to fit within the shadow of the
telescope's secondary mirror to minimize obscuration losses.
The optical system has a resolution of 33 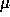 m FWHM
(minimum slit width) at the camera focus corresponding in the
spectral direction to 13.2 Å in first order and 6.6 Å in
second order, and in the spatial direction to 1.2 arcsec.
m FWHM
(minimum slit width) at the camera focus corresponding in the
spectral direction to 13.2 Å in first order and 6.6 Å in
second order, and in the spatial direction to 1.2 arcsec.
- Detector.
- The detector for FOS-2 is a GEC(EEV) P8603 CCD coated
by ESO to enhance the blue response. This chip is described in more
detail in Chapter
 . The CCD is mounted inside the camera
body, and is cooled via a copper cold finger leading to a cryostat
bolted to the side of the instrument. There are plans to upgrade
this to a thinned but otherwise similar chip.
. The CCD is mounted inside the camera
body, and is cooled via a copper cold finger leading to a cryostat
bolted to the side of the instrument. There are plans to upgrade
this to a thinned but otherwise similar chip.
- The cryostat
- contains sufficient liquid nitrogen to keep the
CCD cool for more than 12 hours, and is bolted to the side of the FOS frame,
connecting via a copper cold finger through the side of the camera
body to the CCD. It could be cooled to 120K, but is normally
operated at 150K, stability being achieved using a small heater.
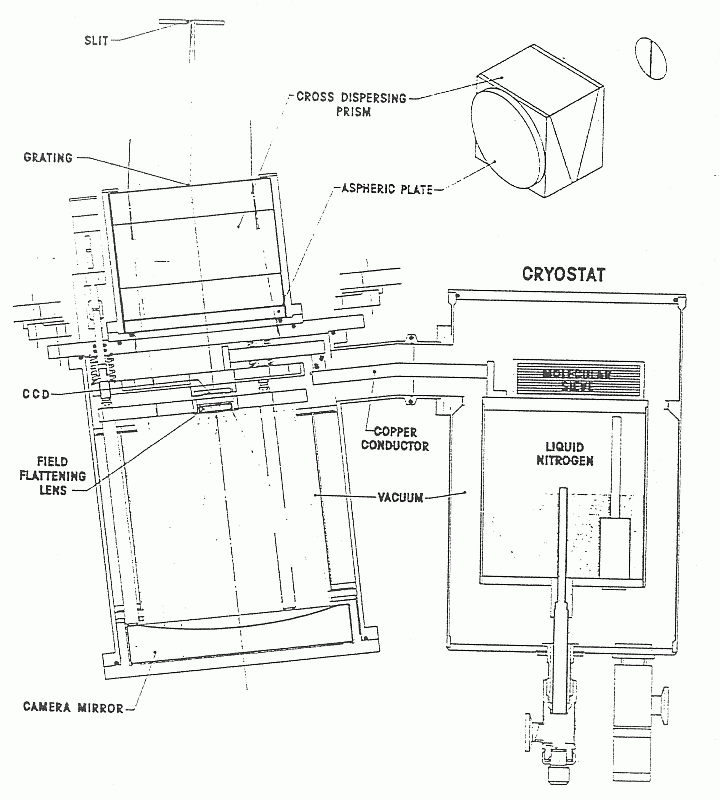
[ TIFF ]
Figure: FOS



Next: Performance
Up: Faint Object Spectrograph
Previous: FOS-1
Tue Aug 15 16:42:46 BST 1995
 ).
).
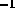 in first order and 200 Å mm
in first order and 200 Å mm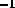 in second order.
The camera consists of an aspheric corrector plate cemented
to the underside of the grism/prism assembly and the silver-coated
spherical mirror. A field flattening lens produces a flat focal
plane at which the detector surface is located. The detector
package is small enough to fit within the shadow of the
telescope's secondary mirror to minimize obscuration losses.
The optical system has a resolution of 33
in second order.
The camera consists of an aspheric corrector plate cemented
to the underside of the grism/prism assembly and the silver-coated
spherical mirror. A field flattening lens produces a flat focal
plane at which the detector surface is located. The detector
package is small enough to fit within the shadow of the
telescope's secondary mirror to minimize obscuration losses.
The optical system has a resolution of 33 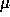 m FWHM
(minimum slit width) at the camera focus corresponding in the
spectral direction to 13.2 Å in first order and 6.6 Å in
second order, and in the spatial direction to 1.2 arcsec.
m FWHM
(minimum slit width) at the camera focus corresponding in the
spectral direction to 13.2 Å in first order and 6.6 Å in
second order, and in the spatial direction to 1.2 arcsec.
 . The CCD is mounted inside the camera
body, and is cooled via a copper cold finger leading to a cryostat
bolted to the side of the instrument. There are plans to upgrade
this to a thinned but otherwise similar chip.
. The CCD is mounted inside the camera
body, and is cooled via a copper cold finger leading to a cryostat
bolted to the side of the instrument. There are plans to upgrade
this to a thinned but otherwise similar chip.